Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing Worked Examples
The selling price is fixed at 35 per unit. In 2016 the company reported the following costs.
Income Statements Under Marginal And Absorption Costing Basic Concepts Of Financial Accounting For Cpa Exam
It leads to over absorption or under absorption of overheads.
. B Since fixed factory overhead is absorbed as a period cost increasing or reducing production and differences in the number of units. Counting on Fingers by AfghanistanMatters is licensed with CC. I Break-even point expressed in rupee sales.
There is also a variable selling cost of 1 per unit and fixed selling cost of 2000 per month. Absorption and Marginal Costing - Worked Examples. Formula Absorption Rate per unit.
Following information are available for the year ended 30 June 2016. Prepare income statement for the year ended 30 June 2016 based on both marginal. Mixed costs can be.
The total cost involved in the making of those sedans was 180000. Absorption vs Marginal Costing Example 1 This example comes from Drury Unit selling price 10 Unit variable cost 6 Fixed manufacturing cost per period 300000 Non-manufacturing costs per period 100000 The company makes one product. Absorption costing produces higher profits than marginal costing in periods of increasing stocks.
In periods of decreasing stocks marginal costing produces higher profits than absorption costing. He manufactured 10 four-wheelers worth 400000 in the first year of business. Statement to Reconcile Profits under Marginal and Absorption Costing Format.
Costs are worked and marginal absorption costing and amended cost object and use the marginal costing be treated as new fixed costs are often used. Installation of Cost Accounting System requires the maintenance of many costing records. Marginal cost of production 5 8 2 15.
A business sells ice cream. The profit margin 15 12 3 per unit. Here we will now examine a worked example to illustrate how a statement of profit can be prepared using marginal costing The Question Zambe Ltd produces one product desks Each desk is budgeted to require 4 kg of wood at 3 per kg 4 hours of labour at 2 per hour and variable production overheads of 5 per unit.
Cost Accounting fails to solve the problems relating to work study time and motion study and operation research. Illustration 2 Marginal Costing Operating Statement under Marginal Costing for the year ended 31 December 2009 Sales 10000 units at 200 each 2000000 Less. A Business Decision Emphasis ACCFIN1007 Uploaded by.
Absorption costing on the other hand takes both fixed costs and variable costs into account. Sam owns an automobile company. Absorption vs marginal costing example this example comes from drury 10 unit selling price unit variable cost fixed manufacturing cost per period costs per.
Variable Selling Overheads 187500 Total Contribution Margin 972500 Less. Fixed factory overheads 1000000 per year. Absorption Costing Income Statement Format.
The following data of x ltd is provided to youopening stock 20000 units valued at marginal costing shs 123800 and total costing shs. MARGINAL COSTING Marginal costing draws a distinction between fixed and variable cost being in are example that standard variable cost was 1130 per. Marginal cost 2500016000 156.
The difference is due to the different treatment of fixed costs in stock valuation. Here is a marginal costing example with the step-by-step calculation. Marginal costing can be classified as fixed costs and variable costs.
During the first two months Zambe expects the following levels of activity. Fixed costs are treated as a period cost and are charged in full to the profit and loss. Planning forecasting and decision making.
Fixed selling costs 400000 per year. Fixed production overheads are budgeted at 20000 per month and average production is estimated to be 10000 units per month. Variable costs per unit.
But the price of 15 could be too high or too low in comparison to the competitors in the market. The variable cost per unit is a constant value. Marginal costing is a cost management technique that is used to determine the total cost of production.
Example of Absorption Costing. Variable Cost of Sales 840000 Product Contribution Margin 1160000 Less. If the management sets the price at 15.
Absorption costing can be classified as production distribution and selling administration. For your reference the following diagram gives an overview of costs that go into absorption costing compared to variable costing. Marginal and absorption costing compared Look back at the information contained in the question entitled.
Ii Number of units that must be sold to earn a profit of Rs. If Absorption is higher then add the figure to the Marginal profit to get the Absorption Costing profit. If Marginal is higher deduct the figure to get the Absorption Costing profit.
Full cost of production 20 as above Difference in cost of production 5 which is the fixed production overhead element of the full production cost. Company A is a manufacturer and seller of a single product. Total Cost per unit 10 2 12 per unit.
Budgeted activity is for 150000 items to be made each period. A For profit planning purposes management requires cost volume profit relationship data which are more readily available from direct cost statement than from absorption costing. Fixed costs per unit 10000 1000 10 per unit.
Absorption costing is the full costing method. Absorption costing refers to the technique that allocates or apportions the total costs incurred to various cost centers to separately determine the cost of production in relation to each cost center. Variable selling cost Rs.
Fixed cost are costs that remain same in total in each period. Marginal costing is a costing method that considers the change in cost for producing one additional unit. Arguments for the use of direct costing include the following.
It considers the change in cost against the change in production level. The main uses are. This means that each unit of opening and closing inventory will be valued at 5 more under absorption costing.
In marginal costing fixed production overheads are not absorbed into products costs. The purpose of marginal costing is to show forth the contribution of the product cost. Variable manufacturing cost Rs.
Fixed Manufacturing Overheads 300000. If Absorption Costing Definition Marginal Product Formula Example 1. Closing inventories of work in progress or finished goods are valued at marginal variable production cost.
In the second year he sold 20 vehicles worth 800000. Costs are either fixed or variable costs.
Difference Between Absorption Costing And Marginal Costing Difference Between

Marginal Costing With Simple Examples
Income Statements Under Marginal And Absorption Costing Basic Concepts Of Financial Accounting For Cpa Exam
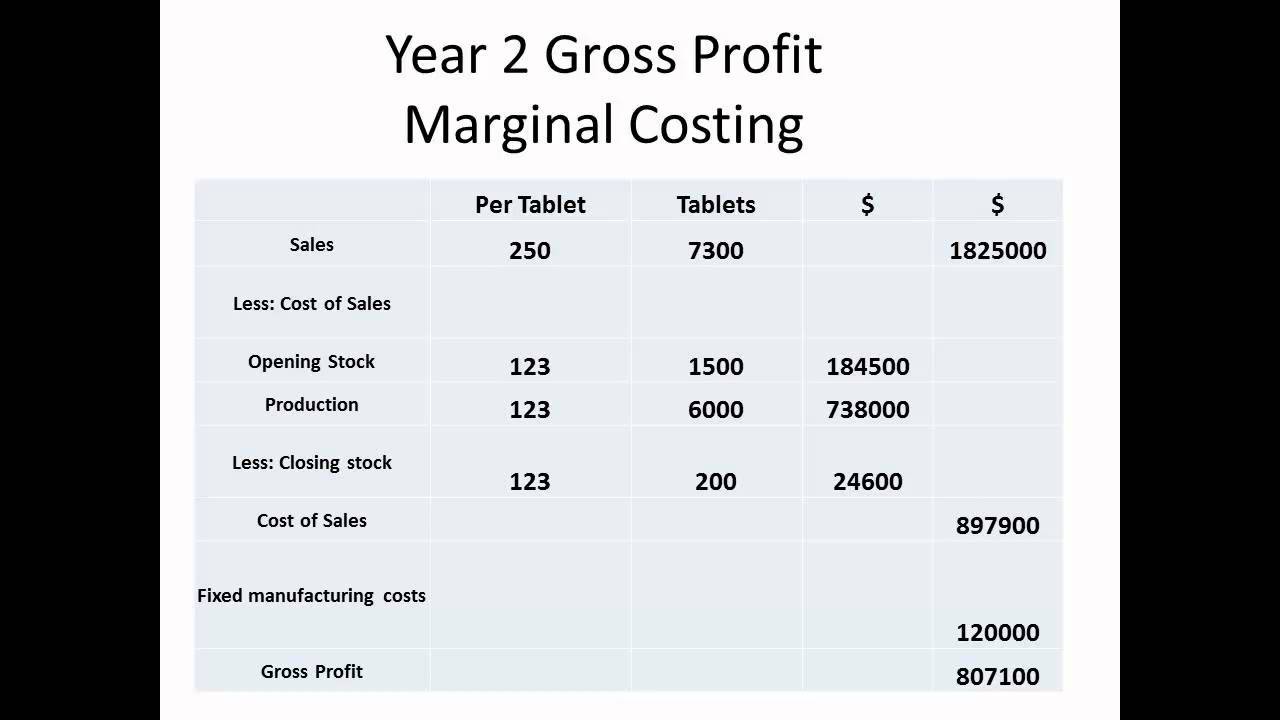
Comments
Post a Comment